Facts About Suboxone
Facts About Suboxone
Suboxone is a prescription pain medication used for the treatment of opiate addiction and withdrawal. Suboxone is effective on any opiate addiction including an addiction to heroin, oxycontin, oxycodone, methadone, percocet, vicodin and morphine. This drug can only be prescribed by doctors and is usually only one part of a larger drug rehabilitation process.
Suboxone is either taken in a pill form, or through a suboxone film, which is both administered under the tongue until it is dissolved. Another form of Suboxone is known as Subutex, which is basically the same drug but without the ingredient Naxolone, which helps to prevent abuse. Both versions of the drug contain Suboxone’s primary ingredient Buprenorphine, which is used specifically for the treatment of opiate withdrawal.
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is the main active ingredient in Suboxone and is itself a partial opiate agonist. This means that it does itself partially contain opiates, which helps to limit cravings and reduce opiate withdrawal symptoms in the patient. Buprenorphine is also widely accepted as a safer alternative to Methadone and comes with a lower chance of addiction and dependency. Buprenorphine also comes with a built-in dosage ceiling, which limits the slight feeling of euphoria the drug can give off, as to prevent abuse.
How Suboxone is Used
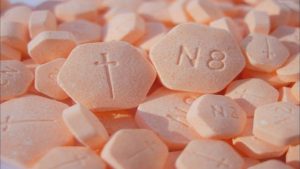 Suboxone can be obtained through a prescription from a Doctor, or medical professional at a drug rehab facility. Suboxone will first be administered by a doctor at the doctor’s office or clinic, but then can be taken at home for the duration of the treatment. Most individuals will start off taking a small dosage of 8-24 mg where they may be under 24 hour monitoring to make sure the patient doesn’t overdose and the medication is working. The patient then will be able to take the medication from the comfort of their own home for the duration of the treatment with a daily dosage of around 12-16 mg. Suboxone may be increased or decreased until the final goal of eliminating withdrawal symptoms has been achieved. From there the doctor will wean the patient off of Suboxone, where they will likely begin the next step in their treatment process.
Suboxone can be obtained through a prescription from a Doctor, or medical professional at a drug rehab facility. Suboxone will first be administered by a doctor at the doctor’s office or clinic, but then can be taken at home for the duration of the treatment. Most individuals will start off taking a small dosage of 8-24 mg where they may be under 24 hour monitoring to make sure the patient doesn’t overdose and the medication is working. The patient then will be able to take the medication from the comfort of their own home for the duration of the treatment with a daily dosage of around 12-16 mg. Suboxone may be increased or decreased until the final goal of eliminating withdrawal symptoms has been achieved. From there the doctor will wean the patient off of Suboxone, where they will likely begin the next step in their treatment process.
Side Effects
Suboxone is itself a partial opiate, so it does come with the risk of addiction and dependence. Suboxone can cause severe allergic reactions such as hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, decreased respirations, confusion and yellowing of the eyes. If any of these side effects occur immediately contact your Suboxone provider. Other mild side effects include headache, stomach pain, insomnia, nausea, sweating and constipation.





